Algorithm/개념
[자료구조] 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)
sangyunpark
2023. 9. 29. 19:56
우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)
우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나옴
- 모든 데이터에 우선순위가 있음
- Dequeue시, 우선순위가 높은 순으로 나감
- 우선순위가 같은 경우에는 FIFO
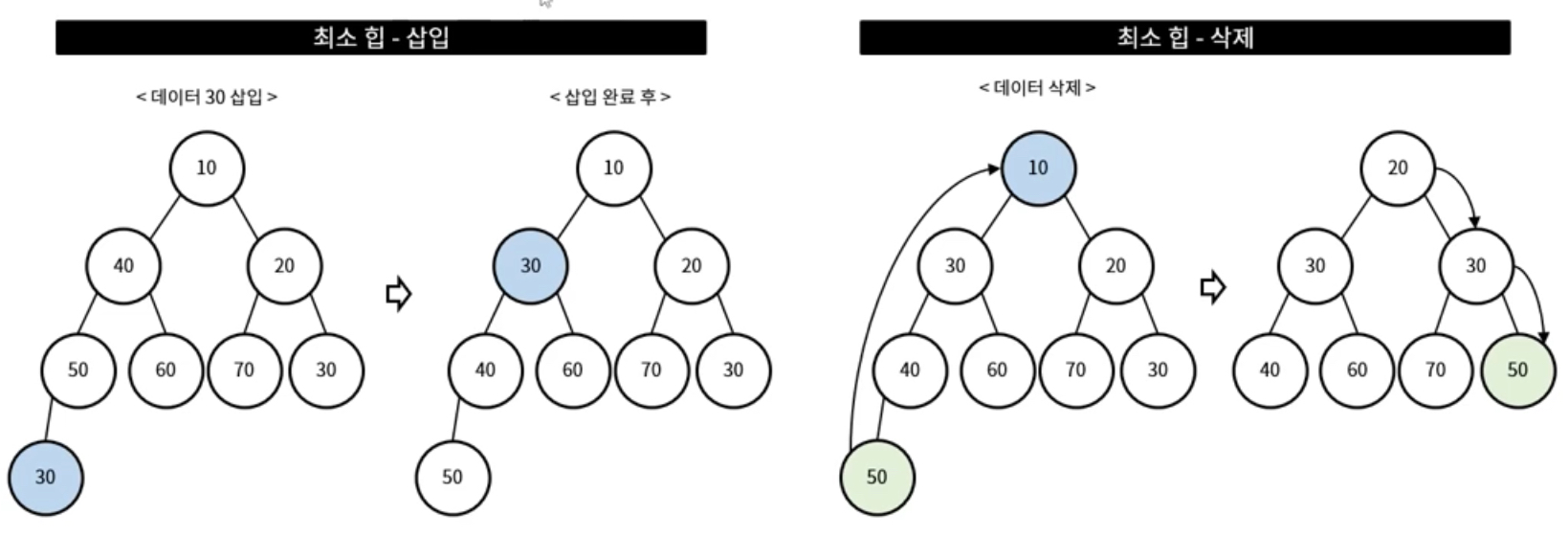
최소 힙, 최대 힙의 삽입, 삭제와 같다.
우선순위 큐 - 구현
(1) 배열
(2) 연결 리스트
(3) 힙
| enqueue() - 값을 넣는 경우 | dequeue() - 값을 빼는 경우 | |
| 정렬된 배열 | O(N) | O(1) |
| 정렬된 연결 리스트 | O(N) | O(1) |
| 힙 | O(logN) | O(logN) |
LinkedList로 우선순위 큐 구현해보기
package org.example.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Main {
public static void enqueue(LinkedList<Integer> list, int data){
int idx = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(list.get(i) > data){
idx = i;
break;
}
}
list.add(idx,data);
}
public static Integer dequeue(LinkedList<Integer> list){
if(list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
int data = list.get(0);
list.remove(0);
return data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 오름차순으로 데이터가 나올 수 있게
LinkedList<Integer> pqList = new LinkedList<>();
enqueue(pqList,5);
enqueue(pqList,7);
enqueue(pqList,3);
enqueue(pqList,1);
enqueue(pqList,9);
System.out.println(pqList); // 1,3,5,7,9
// 자바 기본제공 PriorityQueue - 우선순위 : 값이 작은 순서대로
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(5);
pq.add(7);
pq.add(3);
pq.add(1);
pq.add(9);
System.out.println(pq);
// 우선순위 : 값이 큰대로
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); // reverseOrder를 사용하면 된다.
pq2.add(5);
pq2.add(7);
pq2.add(3);
pq2.add(1);
pq2.add(9);
System.out.println(pq2);
}
}
응용 - 나이로 정렬해보기
클래스 비교시 람다식으로 비교조건 삽입 가능
package org.example.Practice1;
// PriorityQueue 응용
// 나이 순으로 오름차순 또는 내림차순 출력
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Person {
//class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// @Override
// public int compareTo(Person o) {
//
// // 1이 return이 되는 경우 변경 x
// // -1이 반환이 되면 변경한다.
//
// // 새롭게 추가하는 데이터가 더 적을때 변경( 적은 값이 위로 올라감, 오름차순)
// // this.age : 새롭게 들어오는 데이터, o.age 기존의 데이터
// return this.age >= o.age ? 1 : -1;
//
// // 새롭게 추가하는 데이터가 더 클 때 변경( 큰 값이 위로 올라감, 내림차순)
// // return this.age <= o.age ? 1 ; -1;
// }
}
public class Main {
public static void solution(String[] name, int[] age){
PriorityQueue<Person> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
// for (int i = 0; i < name.length; i++) {
// pq.offer(new Person(name[i],age[i]));
// }
//
// while(!pq.isEmpty()){
// Person p = pq.poll();
// System.out.println(p.name + " " + p.age);
// }
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] name = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
int[] age = {30,20,45,62,35};
solution(name,age);
// 기준을 람다식으러 넣어주어도 된다.
PriorityQueue<Person> pq2 = new PriorityQueue<>((Person p1, Person p2) -> p1.age >= p2.age ? 1 : -1);
for (int i = 0; i < name.length; i++) {
pq2.offer(new Person(name[i], age[i]));
}
while(!pq2.isEmpty()){
Person p = pq2.poll();
System.out.println(p.name + " " + p.age);
}
}
}
이름을 기준으로 정렬해보기 - compareTo 활용
package org.example.Practice2;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Person2 {
String name;
int age;
public Person2(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void solution(String[] name, int[] age){
// compareTo : 오름차순으로 구성
PriorityQueue<Person2> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((Person2 p1, Person2 p2) -> p1.name.compareTo(p2.name));
for (int i = 0; i < name.length; i++) {
pq.offer(new Person2(name[i],age[i]));
}
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
Person2 p = pq.poll();
System.out.println(p.name + " " + p.age);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] name = {"A", "B", "C", "D", "E"};
int[] age = {30,20,45,62,35};
solution(name,age);
}
}